Navigating the Evolving Landscape of Digital Accessibility
What is Digital Accessibility and Why Is It Important?
Digital accessibility is an important and ever-evolving topic that affects everyone using the web, applications and any service that is internet related.
With the rise of technology and the Internet, more people rely on digital products and services to communicate, work, and stay connected. As a result, companies have started to make their digital products accessible to all users regardless of their abilities or disabilities. This means staying informed about changes in the digital accessibility landscape so everyone can benefit from this technology.
Businesses need to stay informed about changes in this landscape because it helps them guarantee their products comply with the latest standards and provides them with a competitive advantage when it comes to attracting new customers. Furthermore, staying in touch with the industry changes in digital accessibility can ensure that all web and digital products are usable by all users regardless of any visual, auditory or motor impairments they may have.
In this article, we will provide an overview of the current state of digital accessibility and discuss why it is vital to always stay up-to-date.
Web & Digital Accessibility: A Retrospective
Web & Digital Accessibility have come a long way since the early days of the internet. From the first accessibility initiatives to current laws and regulations, there have been numerous milestones in improving access for people with disabilities all over the world. But despite this progress, only 3% of the internet is completely accessible and compliant, leaving disabled users still faced with many challenges when it comes to using technology.
The evolution of web and digital accessibility has taken many years to date, starting with early disability rights activists pushing for increased access to technology in the 1990s to today’s web standards that ensure websites are accessible to all users regardless of their ability or disability.
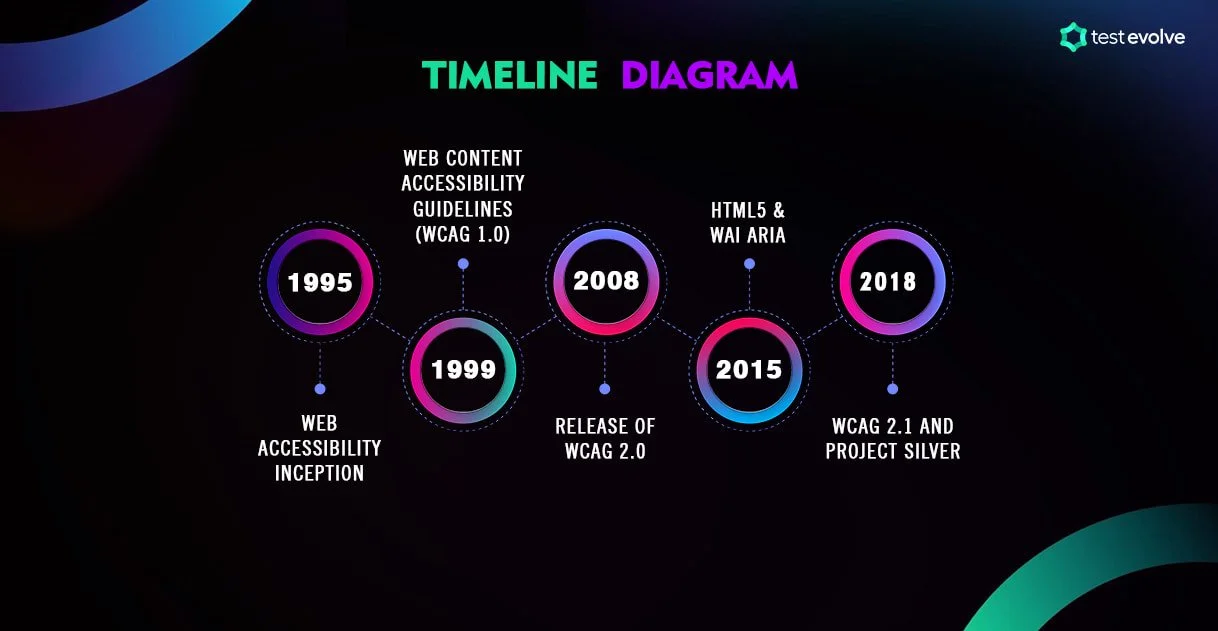
Here is a brief timeline of the most important milestones in Web & Digital Accessibility.
1995: Web Accessibility Begins
n 1995, web accessibility initiatives began to unlock a new wave of internet accessibility for all, regardless of physical or cognitive abilities.
The World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) started to transform the web as we knew it, particularly for those with disabilities, by creating and implementing the first guidelines for web accessibility. Their aim was to confirm that websites were accessible to all users and were compatible with traditional computers and input devices.
Since then, there have been numerous advancements in web accessibility technology that have made things easier for disabled users. Screen readers and voice recognition software have revolutionised how people interact with the Internet, making it possible for a broader range of users to access the web.
1999: WCAG 1.0 Released
1999 saw the release of the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines 1.0, which was a major milestone in the history of web accessibility. This document set out to provide web developers with guidelines for making their websites more accessible.
It was created by the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) and was based on research from various disability organisations and experts in web accessibility. WCAG 1.0 has since been replaced by more recent versions, but it still remains an important document that laid down the foundation for future advancements in web accessibility.
2008: WCAG 2.0 Released
WCAG 2.0 was released in 2008, providing an update to WCAG 1.0 for clearer guidance on how to make web content more accessible and included new requirements for audio-only and video-only content. It also introduced the concept of "conformance levels" that allowed developers to identify the level of accessibility they were aiming for when creating their websites: A (lowest), AA (mid-range), and AAA (highest)
Did you know? WCAG 2.0 was introduced in 2008, the same year the iPhone was launched. It wasn't until 2009 that this technology became accessible to visually impaired individuals, as the guidelines for mobile content were not yet in place.
2015: HTML5 & WAI ARIA
In 2015, HTML5 and WAI-ARIA (Accessible Rich Internet Applications) were introduced as the new standard for web development. This new technology allowed developers to create accessible sites while adding an interactive element to them and enriching the complexity of web applications cross-device. This technology helped improve the UX by providing better navigation and improved SEO.
2018: WCAG 2.1 and Project Silver
WCAG 2.1 and Project Silver were added in 2018. WCAG 2.1 aimed to fill the gap in mobile content guidelines, helping developers comply with accessibility standards when developing mobile websites and responsive designs for web content with 17 new success criteria.
Project Silver focused on integrating accessibility standards into IoT (Internet of Things). This innovative technology makes it possible for everyone to access internet-connected home devices such as refrigerators, climate control systems and security monitoring.
With the implementation of these two initiatives, accessibility has reached a significant milestone.
Did you know? Project Silver got its name from the chemical symbol for silver, "Ag," which is also an abbreviation for Accessibility Guidelines.
Digital Accessibility Trends and Developments in 2023
In 2023, accessibility will be one of the most important web design focuses. As more and more companies commit to and are legally obliged to make their websites accessible to everyone, digital accessibility tools are becoming increasingly important.
With AI-powered tools, increased mobile accessibility, and the rise of inclusive design principles, companies have more and more means to make their websites meet the highest standards of accessibility.
AI-powered tools for Enhanced Accessibility
It is truly amazing how AI-powered accessibility tools are revolutionising the way in which people with disabilities interact with technology. AI-enhanced tools provide users with personalised experiences, making it much simpler for them to access websites, apps, and other digital content.
This is an incredible development that is making a real difference in the lives of those with disabilities, allowing them to access the same technology as everyone else and enjoy the same opportunities.
In the development and testing space, AI is being used to detect and alert about potential accessibility issues in digital content and applications, helping developers to make their products inclusive for all their customers. As AI becomes more powerful, products become more accessible and increasingly compliant with regulations.
Increased Mobile Accessibility
With more and more people using their mobile devices for a variety of daily tasks (from banking, payments, shopping and entertainment), it's essential for businesses to make sure their websites and apps are optimised for mobile. Going mobile-friendly offers numerous advantages to companies and website developers.
It not only increases customer satisfaction and expands their reach, but also helps them succeed and stay ahead in the competitive digital world while being more inclusive for people with disabilities and impairments.
Did you know?: clickable elements should be at least 40px by 40px to accommodate those with motor disabilities or shaky hands and sometimes mobile websites are being tested with elbows instead of fingers for scrolling and navigating.
Inclusive Design Principles
Inclusive design is the new rising star of accessibility. This design philosophy focuses on creating products and services that are accessible to people of all abilities, backgrounds, and genders. The Principles for Inclusive Design are:
Provide comparable experience
Consider situation
Be consistent
Give control
Offer choice
Prioritise content
Add value
Applying these inclusive design principles will be beneficial to all those that are involved in the design and development of websites and applications. This includes, but is not limited to, designers, testers, user experience professionals, developers, product owners, idea makers, innovators, artists, and thinkers.
VR & AR Technologies
Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) technologies have the potential to revolutionise digital accessibility. By employing these technologies, users can access content in a more immersive way, allowing them to experience content more realistically and engagingly.
VR and AR technologies can be used to create interactive experiences for people with disabilities. This could include virtual tours of inaccessible places or enhanced audio-visual experiences for visually impaired people; the possibilities are endless for using VR and AR technologies for digital accessibility.
5G & IoT
The advent of 5G and IoT technology has drastically improved the field of digital accessibility. It has enabled people with disabilities to access digital services and content more efficiently than ever before. 5G provides faster, more reliable internet connectivity, allowing users to access websites, apps, and other online resources easily.
Furthermore, 5G and IoT offer a wide range of use cases in areas such as healthcare, education, transportation, and entertainment. This makes it easier for disabled people to take advantage of the latest technologies to improve their lives. With the help of this technology in digital accessibility, we can ensure that everyone has an equal opportunity to access all the benefits that modern technology has to offer.
Digital Accessibility FAQs
-
The purpose of digital accessibility is to ensure that digital products, such as websites and mobile applications, can be used by individuals with disabilities.
-
The Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) are a set of guidelines developed by the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) that provide a framework for creating accessible web content.
-
Digital accessibility benefits everyone, not just individuals with disabilities. Many accessibility features, such as clear and concise content, easy-to-use navigation, and high-contrast colors, improve the user experience for all users.
-
Organizations can achieve digital accessibility by following the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG), which provide a set of standards for making digital content and technology accessible.
-
Digital accessibility can benefit businesses in several ways. By making their digital products accessible, businesses can:
Expand their customer base by reaching individuals with disabilities.
Improve their reputation and brand image by showing their commitment to diversity and inclusivity.
Increase customer loyalty by providing a positive user experience for all users.
Comply with legal requirements and avoid legal penalties.
-
Some common accessibility features that can be implemented to make digital products more accessible include:
Alternative text for images, which provides a text description of the image for users who cannot see it.
Captions and transcripts for audio and video content, which provide a text-based alternative for users who cannot hear it.
Keyboard navigation, which allows users to navigate through the website or application using only the keyboard.
High contrast colors, which make it easier for users with low vision to distinguish between different elements on the page.
Automated vs Manual Accessibility Testing – Understanding the Difference | Webinar Alert
Let’s get some clarity on why both are critical for your compliance.
Regardless of your chosen automated Accessibility Testing tooling, you can still only hope to assess you application for a maximum of 50-60% of all potential Accessibility violations.
This means that for the remaining 40-50%, you need to be able to assess your application manually.
In this webinar, we’ll look at automated versus manual coverage and how you can bring both together to present a unified picture of your application’s compliance to WCAG 2.2 standards.
Thu, 10 Oct 2024 17:00 - 18:00 BST
Few seats left—click here to reserve your spot today!
Conclusion
Accessibility is the Digital World’s big focus. From website design to app creation, it’s essential that people with disabilities are able to interact with these technologies.
We discussed the various standards and guidelines available to provide digital accessibility, as well as some of the challenges and solutions associated with it. Looking ahead, we can expect more technological advancements that will allow people with disabilities greater access to digital products and services.
Achieving true digital accessibility in practice can be challenging due to usability issues with assistive technology (AT) tools, gaps in access to technology due to the digital divide, and other barriers.
It is important for everyone – developers, designers, testers and users alike to stay informed about new developments so that we can continue creating a more inclusive digital landscape for all people.
All these factors combined will make 2023 a great time for web design and development with a focus on accessibility!